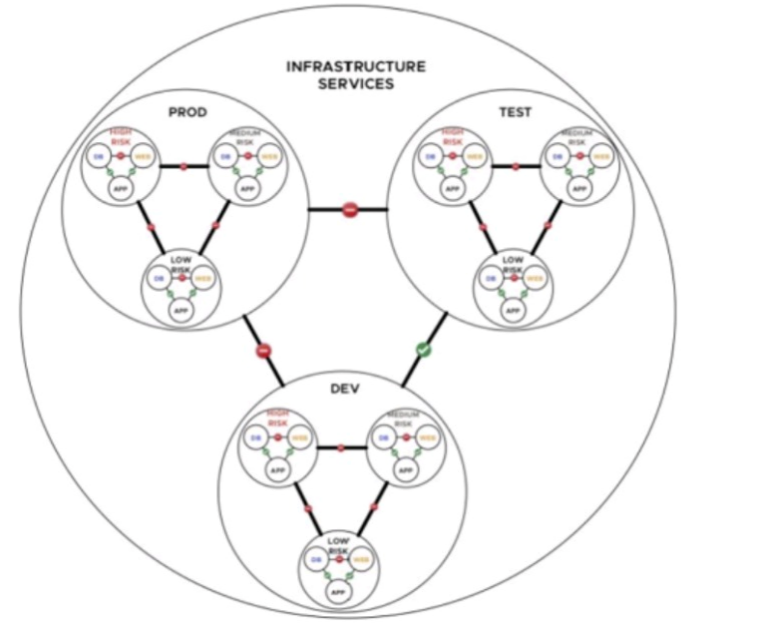
1. Understanding the Exhibit and NSX Security Segmentation
The diagram represents NSX-T logical segmentation for a microservices-based financial company.
It categorizes workloads into three distinct risk levels:
High Risk (Red)
Medium Risk (Yellow)
Low Risk (Blue)
The objective is to enforce security policies with minimal management overhead while maintaining isolation between risk levels.
2. Why 'One Security Policy Per Level of Security' is the Best Choice (B)
Grouping workloads based on security levels (High, Medium, Low) simplifies firewall rule management.
By defining a single security policy per level of security, it reduces the need to create multiple firewall rules for each microservice individually.
Advantages of this approach:
Scalability: New workloads can inherit existing security policies without manual rule creation.
Simplification: Instead of hundreds of firewall rules, a few policies handle traffic isolation effectively.
Automation-Friendly: Security policies can be applied dynamically using NSX-T security groups.
3. Why Other Options are Incorrect
(A - Create One Firewall Rule Per Application Tier)
High overhead and complexity: Each application has its own rule, making it harder to scale as the number of applications grows.
Requires continuous manual rule creation, increasing administrative burden.
Better suited for small, static environments but not scalable for microservices.
(C - Create One Firewall Rule Per Level of Security)
Firewall rules alone do not provide granular segmentation.
A single firewall rule is insufficient to define security controls across multiple application tiers.
Security policies provide a more structured approach, including Layer 7-based controls and dynamic membership.
(D - Create a Security Policy Based on IP Groups)
IP-based security policies are outdated and not scalable in a dynamic microservices environment.
NSX-T supports workload-based security policies instead of traditional IP-based segmentation.
Microservices often use dynamic IP addresses, making IP-based groups ineffective for security enforcement.
4. NSX Security Best Practices for Microservices-Based Designs
Use NSX Distributed Firewall (DFW) for Micro-Segmentation
Apply security at the workload (vNIC) level to prevent lateral movement of threats.
Enforce Zero Trust security model by restricting traffic between risk zones.
Group Workloads by Security Posture Instead of Static IPs
Leverage dynamic security groups (tags, VM attributes) instead of static IPs.
Assign security rules based on business logic (e.g., production vs. development, PCI-compliant workloads).
Use Security Policies Instead of Individual Firewall Rules
Policies provide abstraction, reducing the number of firewall rules.
Easier to manage and apply to multiple workloads dynamically.
Monitor and Automate Security Policies Using NSX Intelligence
Continuously analyze workload communication patterns using VMware Aria Operations for Networks (formerly vRealize Network Insight).
Automate rule updates based on detected traffic flows.