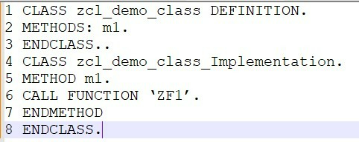
Which statement can you use to change the contents of a row of data in an internal table?
Correct Answer:
B
The statement that can be used to change the contents of a row of data in an internal table is MODIFY table. The MODIFY table statement can be used to change the contents of one or more rows of an internal table, either by specifying the table index, the table key, or a condition. The MODIFY table statement can also be used to change the contents of a database table, by specifying the table name and a work area or an internal table. The MODIFY table statement can use the TRANSPORTING addition to specify which fields should be changed, and the WHERE addition to specify which rows should be changed.
The other statements are not suitable for changing the contents of a row of data in an internal table, as they have different purposes and effects. These statements are:
APPEND table: This statement can be used to add a new row of data to the end of an internal table, either by specifying a work area or an inline declaration. The APPEND table statement does not change the existing rows of the internal table, but only increases the number of rows by one.
INSERT table: This statement can be used to insert a new row of data into an internal table, either by specifying the table index, the table key, or a sorted position. The INSERT table statement does not change the existing rows of the internal table, but only shifts them to make room for the new row. The INSERT table statement can also be used to insert a new row of data into a database table, by specifying the table name and a work area or an inline declaration.
UPDATE table: This statement can be used to update the contents of a database table, by specifying the table name and a work area or an internal table. The UPDATE table statement can use the SET addition to specify which fields should be updated, and the WHERE addition to specify which rows should be updated. The UPDATE table statement does not affect the internal table, but only the corresponding database table.