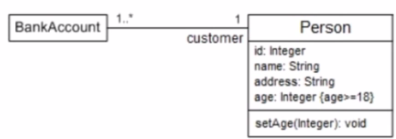
Which category of stakeholders should have prime responsibility for making decisions on the contents of a domain model, and why?
Correct Answer:
B
In the development of a domain model, the prime responsibility for decision-making should ideally rest with the users, as they are the ones who will be using the system operationally. Users have the most direct and frequent interactions with the system, making them best positioned to provide relevant insights into what the system should do and how it should behave to meet their needs effectively. While other stakeholders such as customers, project managers, and developers play significant roles, the users' intimate knowledge of the domain processes and their requirements make them key contributors to ensuring that the domain model aligns closely with real-world application and utility.