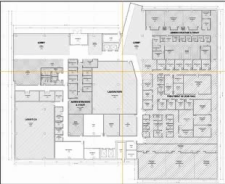
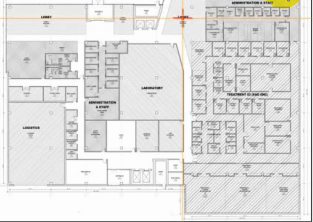
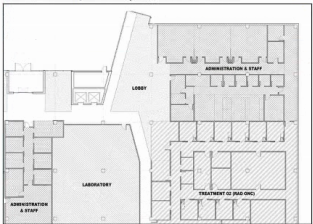
An architect has just received client approval of the Schematic Design documents for a three-story, outpatient medical clinic. The clinic is located within a mixed-use development governed by
a City-approved Planned Development (PD) document. The medical clinic design utilizes standardized departmental layouts and includes outpatient clinics, as well as treatment spaces,
administrative spaces and public/lobby spaces.
The site needs to accommodate four different vehicular traffic flows: patient traffic, staff traffic, service and delivery traffic, and emergency services traffic. In addition, a pedestrian plaza
must connect to the mixed-use development sidewalks. The plaza must provide space for bicycle parking and will serve as the future bus stop.
The site design addresses several challenges related to building orientation. The southeast facade, with excellent visibility from the highway, is the location of all service equipment. The
building entrance faces northwest, convenient to the parking but not visible from the highway.
The client believes future patient volumes will outgrow the clinic. The PD document allows for a planned Phase 2 development on the adjacent vacant site to the southwest. Phase 2 would
include a second building (2 story, 80,000 BGSF) and/or a parking deck.
Other considerations for the project include:
Protected tree requirements are defined in the PD document.
Easy pedestrian access must be provided from Sycamore Boulevard.
All required parking for the clinic must be accommodated on site.
Programmed area includes 109,450 Departmental Gross Square Feet (DGSF) / 130,184 Building Gross Square Feet (BGSF).
Exterior material percentages are dictated by the PD document and shall not exceed specific percentages for Primary and Secondary Finishes.
All service equipment needs to be screened; see PD document for restrictions.
Signage opportunities are important to the client.
Acoustical privacy is a concern of the healthcare system.
The following resources are available for your reference:
Drawings, including a perspective, plans, and exterior elevations
Building Program, including client's departmental program and detailed program for Treatment 01 (Infusion)
Exterior Material Cost Comparisons
Planned Development Document
IBC Excerpts, showing relevant code sections
ADA Excerpts, showing relevant sections from the ADA Standards for Accessible Design
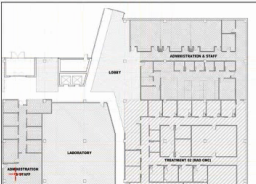
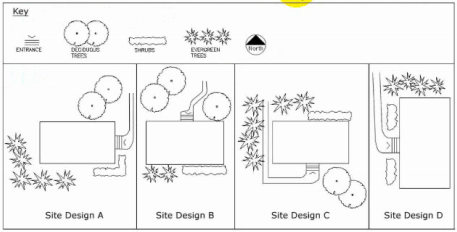
Which of the following design solutions best addresses the client's concerns related to building orientation, vehicular circulation, and future expansion?
Show Answer
Hide Answer
Correct Answer:
B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The design must balance client priorities, regulatory requirements, and site conditions:
Vehicular Circulation:
Separating traffic flows by function reduces conflicts and improves safety---patients, staff, deliveries, and emergency vehicles each require distinct circulation paths.
Building Orientation:
The main entrance facing northwest towards parking prioritizes user convenience, even if this orientation has less highway visibility. The southeast facade, visible from the highway, is dedicated to service equipment screened per PD document restrictions.
Pedestrian Plaza:
Providing a pedestrian plaza connected to mixed-use development sidewalks, with bicycle parking and bus stop, aligns with site accessibility and transit integration goals.
Future Expansion:
Positioning the site elements to accommodate Phase 2 on the adjacent southwest vacant site facilitates growth without major disruption.
Screening and Material Use:
Service equipment screening and adherence to PD exterior material percentages maintain design compliance.
Acoustical Privacy:
The layout supports departmental adjacency and separation for privacy, crucial in healthcare design.
Option B best addresses these concerns and reflects the project's functional, regulatory, and contextual needs as outlined in NCARB ARE 5.0 Project Integration and Site Planning content.
ARE 5.0 Project Planning & Design Content Outline: Project Integration of Program and Systems --- Site Planning and Circulation
City-approved Planned Development Document
ADA Standards for Accessible Design
The Architect's Handbook of Professional Practice, 15th Edition, Chapters 6 and 7 on Site Design and Program Integration