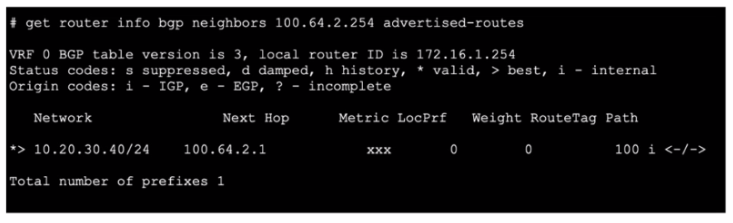
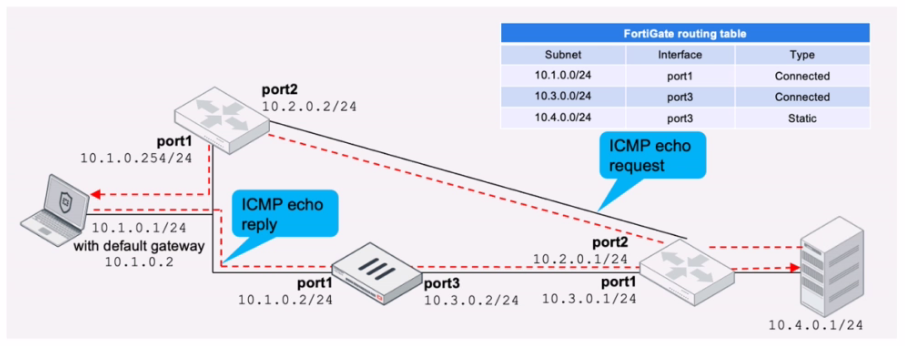
Refer to the exhibit.
FortiGate has already been configured with a firewall policy that allows all ICMP traffic to flow from port1 to port3.
Which changes must the administrator perform to ensure the server at 10.4.0.1/24 receives the echo reply from the laptop at 10.1.0.1/24?
Correct Answer:
C
Current Configuration Analysis:
The firewall policy currently allows ICMP traffic from port1 to port3, enabling the ICMP echo request to reach the server.
However, for the server to send an ICMP echo reply back to the laptop, the traffic must be allowed from port3 to port1.
Required Configuration:
To ensure the server at 10.4.0.1/24 can send the ICMP echo reply back to the laptop at 10.1.0.1/24, the administrator needs to configure a new firewall policy.
The policy must explicitly allow ICMP traffic from port3 to port1.
Steps to Configure:
Access the FortiGate configuration interface.
Navigate to the Firewall Policy section.
Create a new policy allowing ICMP traffic from port3 to port1.
Save and apply the new policy to ensure bidirectional ICMP traffic is permitted.
Fortinet Network Security 7.2 Support Engineer Documentation
FortiGate Firewall Policy Configuration Guides