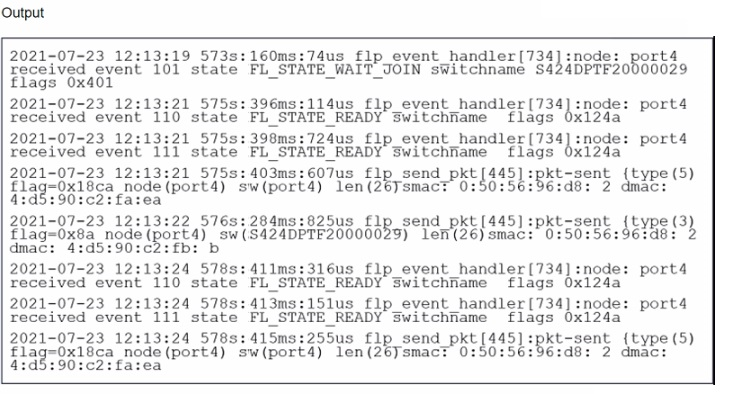
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two statements best describe what is displayed in the FortiLink debug output shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
A, B
The provided debug output indicates that the FortiSwitch is sending FortiLink heartbeats to the FortiGate and is currently waiting to join the stack group. Here's a breakdown of the relevant lines:
Line 1: Shows the date, time, elapsed time since boot, and process ID for the FortiLink event handler.
573s:160ms: 74us translates to roughly 573 seconds, 160 milliseconds, and 74 microseconds since uptime.
Event 101: This indicates the FortiSwitch is in a 'wait join' state (FL_STATE_WAIT_JOIN). This means it's discovered by the FortiGate and is awaiting further instructions to join the FortiLink stack group.
switchname S424DPTF20000029: This displays the serial number of the FortiSwitch.
flags 0x401: The specific flag meaning might depend on the FortiSwitch model and version, but it likely indicates general communication between the switch and FortiGate.
Lines 2 and onward: These lines show subsequent events with similar timestamps, suggesting a regular heartbeat interval. There are also instances of the FortiSwitch sending packets to the FortiGate (indicated by pkt-sent).
Why the Other Options Are Less Likely:
C . FortiSwitch is discovered and authorized by FortiGate. While discovery might have happened before these lines, the 'wait join' state suggests authorization hasn't necessarily completed yet.
D . FortiSwitch is ready to push its new hostname to FortiGate. There's no explicit indication of hostname changes in this excerpt. The focus is on joining the stack group.
In Summary:
The key point is the 'FL_STATE_WAIT_JOIN' state, which signifies the FortiSwitch is ready to be fully integrated but is waiting for further commands from the FortiGate to complete the process.