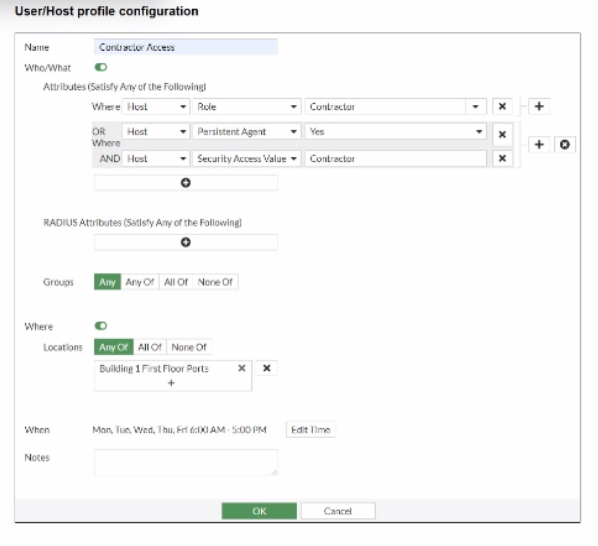
When creating a user or host profile, which three criteria can you apply? (Choose three.)
Correct Answer:
A, B, E
The User/Host Profile is the primary mechanism in FortiNAC-F for identifying and categorizing endpoints to determine their level of network access. According to the FortiNAC-F Administration Guide, a profile is built using a combination of criteria that define 'Who' is connecting, 'What' device they are using, and 'Where' they are located on the network.
The three main categories of criteria available in the configuration are:
Host or User Attributes (B): This includes specific details such as the host's operating system, the user's role (e.g., Employee, Contractor), or custom attributes assigned to the record.
Host or User Group Memberships (A): Profiles can be configured to match endpoints that are members of specific internal FortiNAC groups or synchronized directory groups (like LDAP or Active Directory groups). This allows for broad policy application based on organizational structure.
Location (E): The 'Where' component allows administrators to restrict a profile match to specific physical or logical areas of the network, such as a particular switch, a group of ports, or a specific SSID.
Criteria like an 'applied access policy' (D) are the outcome of a profile match rather than a criterion used to define the profile itself. Similarly, the 'Adapter current VLAN' (C) is a dynamic state that changes based on enforcement and is not a standard static identifier used for profile matching.
'User/Host Profiles are used to identify the hosts and users to which a policy will apply. Profiles are created by selecting various criteria in the Who/What (Attributes and Groups) and Where (Locations) sections. Attributes can include Host Role, User Role, and OS. Group memberships allow matching based on internal or directory-based groups. Location criteria allow for filtering based on the device or port where the host is connected.' --- FortiNAC-F Administration Guide: User/Host Profile Configuration.