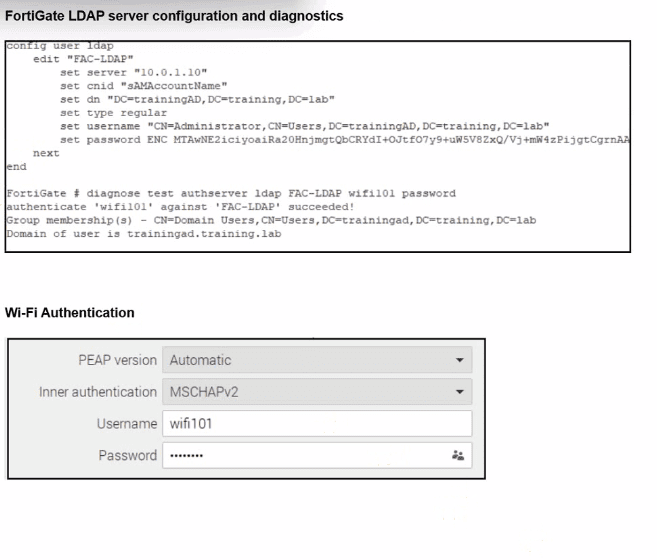
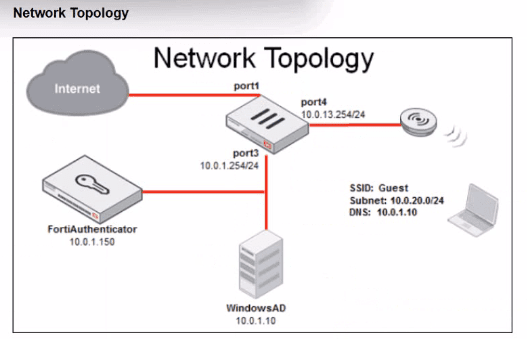
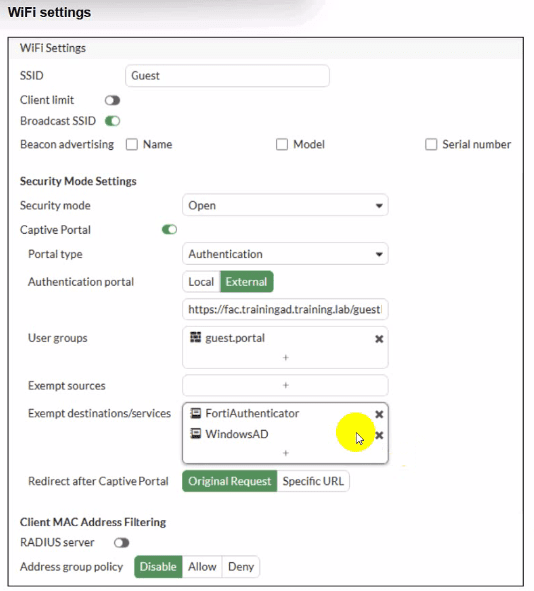
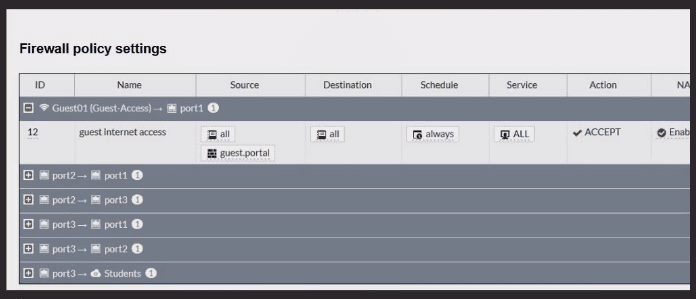
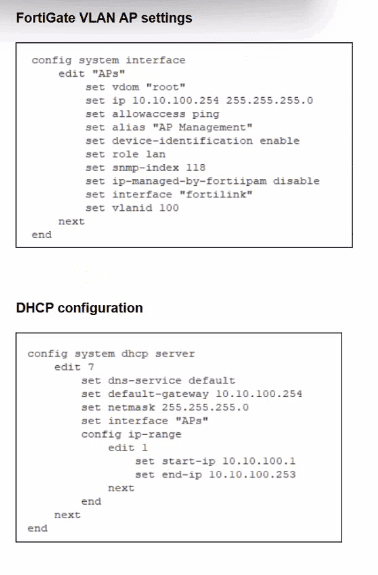
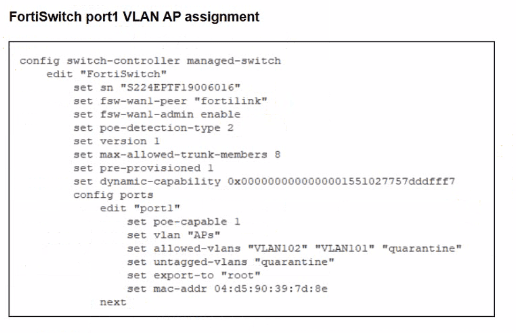
From the exhibits:
SSID ''Guest''
Security mode:Open
Captive Portal: Enabled, portal typeAuthentication External
External portal URL: https://fac.trainingad.training.lab/guest (FortiAuthenticator)
Exempt destinations/services:FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD
Firewall policy
From theGuest interface/zonetoport1 (Internet)
Source user group:guest.portal(authenticated users)
The flow for anexternal captive portalis:
Client associates to theopen Guest SSID.
Client makes an HTTP(S) request.
FortiGate intercepts and redirects the client to theexternal portal.
Client must be able toreach FortiAuthenticator's IP(and AD if the portal needs it)before authentication.
In this setup:
Theexempt destinationsetting tells the captive portal logicnot to require authenticationfor traffic going to FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD.
However, there still must be a firewall policy that allows traffic from the Guest SSID subnet to those exempt destinations.
The existing firewall policy uses theguest.portal user groupas a source condition, which only matchesaftersuccessful portal authentication. Before login, the client has no user identity, so:
Traffic from the unauthenticated Guest client FortiAuthenticator isnot matchedby that policy.
It hits theimplicit deny, so the browser never reaches the login page.
To fix this, the administrator must:
Create or modify a firewall policy thatallows traffic from the Guest SSID subnet/interface to FortiAuthenticator and WindowsAD without requiring user authentication.
That is exactly what optionDdescribes.
Why the others are wrong:
A . Change SSID security mode to WPA2-Enterprise-- External captive portals are normally used withopenSSIDs; WPA2-Enterprise uses 802.1X, not captive portal.
B . Disable HTTPS redirection-- Redirection is required so users are sent to the portal; disabling it doesn't solve reachability.
C . Exclude FortiAuthenticator and Windows AD from filtering-- They're already listed asexempt destinationsin the SSID configuration; the missing piece is thefirewall policy, not the exemption.