An administrator wants to monitor and inspect large amounts of traffic and detect unauthorized attempts from inside the organization, with the help of an IDS. They are not able to
recognize the exact location to deploy the IDS sensor. Can you help him spot the location where the IDS sensor should be placed?
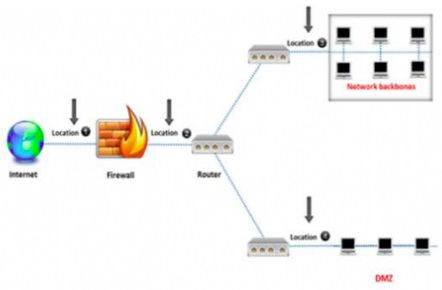
Show Answer
Hide Answer
Correct Answer:
B
In the context of Certified Network Defender (CND), an IDS sensor should be placed at a location where it can effectively monitor and inspect traffic to detect unauthorized attempts. Location 3, which is situated after the firewall but before the network backbone, is ideal for this purpose. At this location, the IDS can analyze traffic that has passed through the firewall, allowing it to focus on potentially harmful traffic that could affect the internal network. It provides visibility into both incoming and outgoing traffic, enabling comprehensive monitoring and detection of any unauthorized or malicious activity.


