Service A provides a data access capability that can be used by a variety of service consumers. The database records accessed by Service A are classified as either private or public. There are two types of service consumers that use Service A:
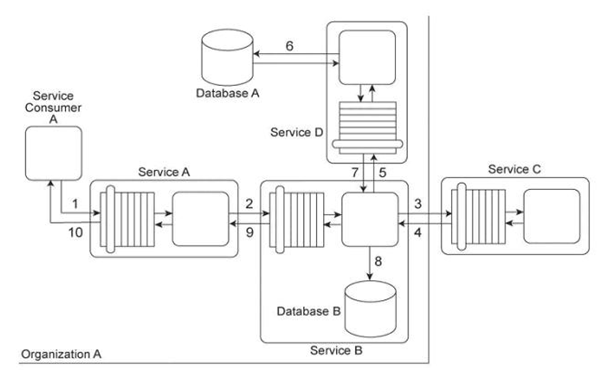
Service consumers with public access permissions (allowed to access only public data records) and service consumers with private access permissions (allowed to access all data records). For performance reasons the Service A architecture uses a single database, named Database A .Each record in Database A is classified as either private or public. After Service A is invoked by a service consumer (1), it authenticates the request message using an identity store and retrieves the corresponding authorization (2, 3). Once authorized, the service consumer's request is submitted to Database A (4), which then returns the requested data (5) If the service consumer has private access permissions, all of the returned data is included in Service A's response message (6). If the service consumer has public access permissions, then Service A first filters the data in order to remove all unauthorized private data records before sending to the response message to the service consumer (6). In addition to retrieving data, Service A's data access capability can be used to update database records. An investigation recently revealed an information leakage problem that can occur when service consumers with public access permissions attempt to update the ID value of a database record The ID values of all database records (private or public) must be unique. When a service consumer with public access permissions updates a public database record with an ID value that is already assigned to a private database record, the database returns an error message describing this conflict. This error text reveals confidential information by stating that the ID value submitted by the service consumer with public access permissions already exists within a private database record. What steps can be taken to avoid this problem while preserving the requirement that all database records (private and public) have unique ID values?

Show Answer
Hide Answer