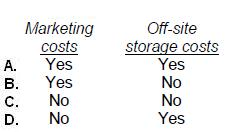Which one of the following will result in an accruable expense for an accrual-basis taxpayer?
Correct Answer:
B
RULE: An accruable expense is one is which the services have been received/performed but have not been paid for by the end of the reporting period.
Choice 'b' is correct. The facts indicate that a repair was completed prior to year end but not yet invoiced. If it has not yet been invoiced, it is assumed that it has also not yet been paid for. Therefore, this is a situation in which the repair expense would be accrued at year end. Services have been performed, but they have not been paid for, as they have not even been invoiced yet.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. If the repair was completed after year end, then the expense is not accruable, as the benefit of the services hasn't been received as of year end. The fact that the repair was invoiced prior to year end does not impact the situation.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. If a repair was completed and paid for prior to year end, no accrual is appropriate. On the accrual basis, the expense is taken in the year the repair is completed and the benefit is received. In this case, the account payable was also paid in the same year, but this has no effect on the expense.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. The facts indicate that the work is to be completed at a date later than year end. Therefore, the expense is not accruable at year end, as the benefit of the repair hasn't been received as of year end. It is reasonable that a signed contract for the repair work exists, but this has no effect on the accrual.