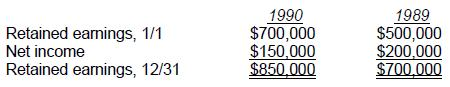An inventory loss from a market price decline occurred in the first quarter, and the decline was not expected to reverse during the fiscal year. However, in the third quarter the inventory's market price recovery exceeded the market decline that occurred in the first quarter. For interim financial reporting, the dollar amount of net inventory should:
Show Answer
Hide Answer
Correct Answer:
C
Choice 'a' is correct. Market price declines should be recognized in the interim period in which decline is judged permanent and later, if they 'turn around,' are recognized as gains in subsequent periods only to the extent of previously reported losses.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Recovery should not cause an increase in inventory value above original cost.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. The recovery should be recognized to the extent of the first quarter write down.
Choice 'd' is incorrect.